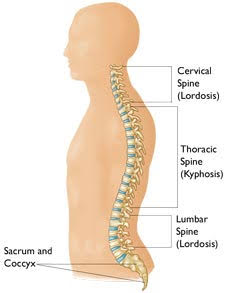
Spine Segments and Curvature and Vertebrae
The spine is made up of three larger segments: Cervical (the neck), thoracic (upper back), and lumbar (lower back) and two smaller segments: Sacrum and coccyx (tailbone). The cervical, thoracic and lumbar parts of the spine are composed of articulating vertebrae and when viewed from the side, these segments form “c-shaped” curves. It is these curves that allow us to stand upright and maintain balance. When these curves are too large or too small, there is a deformity in the spine. These spinal abnormalities are referred to as Kyphosis of the thoracic spine (“hunchback”) and Lordosis of the lumbar spine. Scoliosis is also a spinal abnormality. It is found when the spine forms an “S” or a “C” shape, rather than an “I” when viewing the spine from the front or back. The sacrum and coccyx are composed of vertebrae that are fused together and are not moveable.
Vertebrae
The spine is made up of vertebrae that are stacked on top of one another. These bones form a canal that protects your spinal cord. There are 33 vertebrae in the spine. The upper or movable part of the spine has 24 vertebrae. The cervical spine is made up of 7 small vertebrae that begin at the base of the skull and end at the upper chest. The thoracic spine is made of 12 vertebrae that start at the chest and end at the middle back. The vertebrae in the thoracic spine are also connected to the rib cage. There are 5 vertebrae in the lumbar spine. These vertebrae are larger in size as they carry more of your body’s weight. It is possible to have fewer or more vertebrae in one of these segments. In the lower part of the spine, 5 vertebrae are fused together to form the sacrum and 4 are fused to form the coccyx or tailbone.
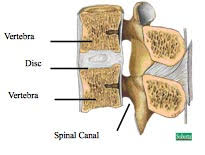
The vertebrae are comprised of various parts that function to support and stabilize the spine while also providing protection for the spinal cord. The vertebral body bears most of the weight of the spine and serves as the attachment to the discs between each vertebra. The pedicles are the two “tube-like” projections connecting the vertebral body in the anterior (front) part of the spine to the posterior (back) part of the spine. The posterior vertebrae can be felt by pressing on your back. The “wings” or projections of the vertebrae are referred to as processes. The spinous process is the projection in the center of the vertebrae. The transverse processes come off of each side of the vertebrae and serve as an attachment to many muscles that help with bending, twisting, and standing still. Between these are small joints called facet joints. They allow you to move. It is possible for these joints to become sore and cause pain.
Spinal Cord And Nerves, Muscles And Ligaments, Intervertebral Disc And Facet Joints
Spinal Cord and Nerves
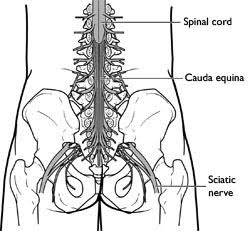
The spinal cord is the center of your body’s nervous system and extends from the skull down to your lower back through the spinal canal. The space inside each vertebra acts as the tunnel through which the spinal cord travels. Nerves branch out from the spinal cord through the openings in the vertebrae and carry messages between the brain and the muscles. The spinal cord ends in the lower back and continues as nerve roots to the legs and feet. This is why symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling are often found in the arms and legs as a result of a spine condition.
Muscles and Ligaments
The muscles and ligaments that are attached to your spine provide support and stability for your spine as well as your upper body. Strong ligaments connect your vertebrae and help keep the spinal column in position.
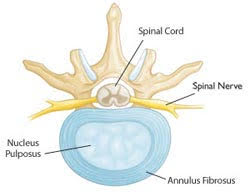
Intervertebral Disks
Between each vertebra, in the moveable part of your spine, are intervertebral disks. They are flat and round and are about a half-inch thick. Each vertebral disk is made of two components: The nucleus pulpous, the jelly-like center of the disk that gives the disk flexibility and strength and the annulus fibrosus, the outer ring of the disk. These disks act as shock absorbers for the spine and help protect the vertebrae from becoming damaged. However, nerve endings supply the disks and as a result, an injury to the disk can cause pain.
Facet Joints
On the posterior side of the vertebrae, between the spinous process and the transverse processes are facet joints. These joints, similar to your hip or knee joints, have a cartilage surface. They allow for the rotation of the spine. However, arthritis or wear and tear in the facet joint can be a source for back or neck pain.
Danger Signals
Not all spinal problems can be grouped as a lifestyle related problem. Presence of some of the following features will need close evaluation by the Spine Specialist:
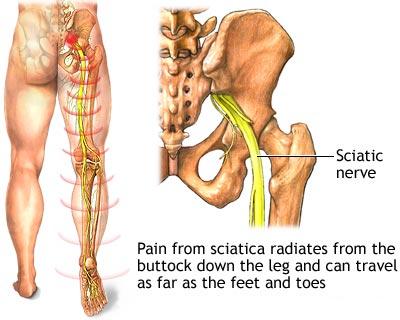
- Low back pain travelling down to lower limbs (Sciatica), Neck pain travelling down to upper limbs or upper back pain travelling towards the chest. The pain may worsen on coughing or sneezing. The presence of this pattern of pain usually signifies a disc prolapse causing compression of the spinal cord or nerve.
- Pain in the thighs, calf or buttocks which worsen with walking and relieves on rest. This symptom called as “neurogenic claudication” is usually due to compression of nerve root or spinal canal stenosis.
- Weakness or numbness in a part of or whole of lower or upper limbs. Slipping off of footwear or inability to grasp with hands
- Unsteadiness while walking or change in pattern of walking. This usually is due to spinal cord compression.
- Deformity or an unusual “hump” in the region of spine needs examination at the earliest.
- Pain in the region of Spine with fever / weight loss / cough
- Pain in the region of spine which is present on rest also.
Appointment : 9945112112
Timing 1pm-2pm and 4pm-6pm. Consultation by appointment only. ( Except Friday & Saturday )
Appointment : 9008518855
Tue | Thu | Sat - Timing 10pm-1pm